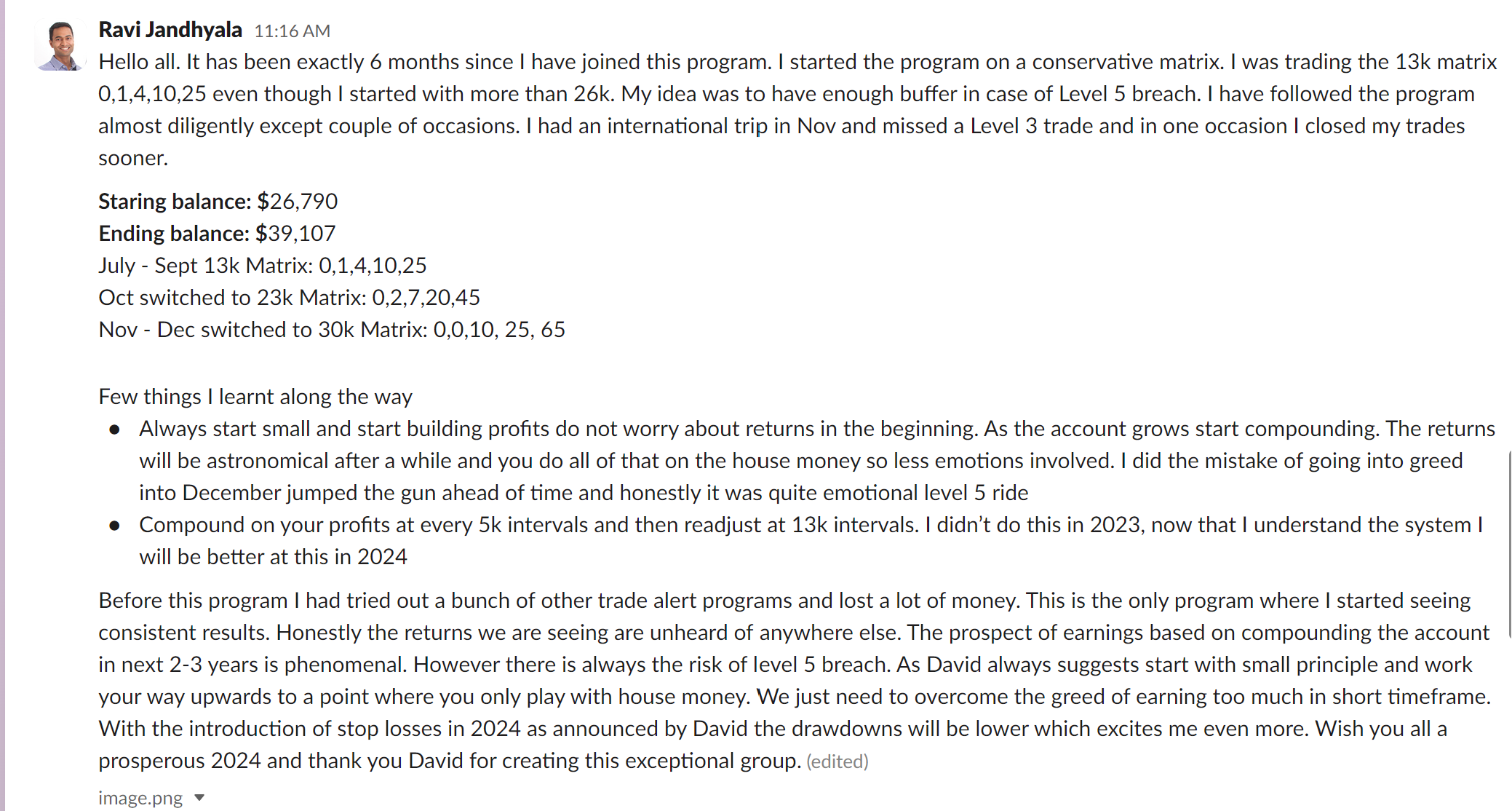
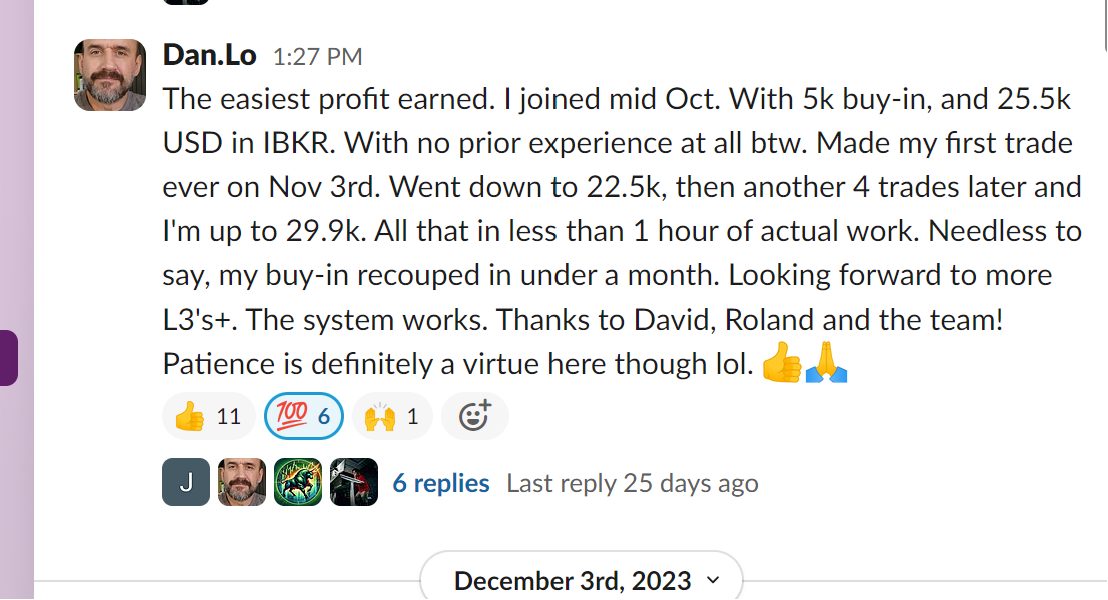
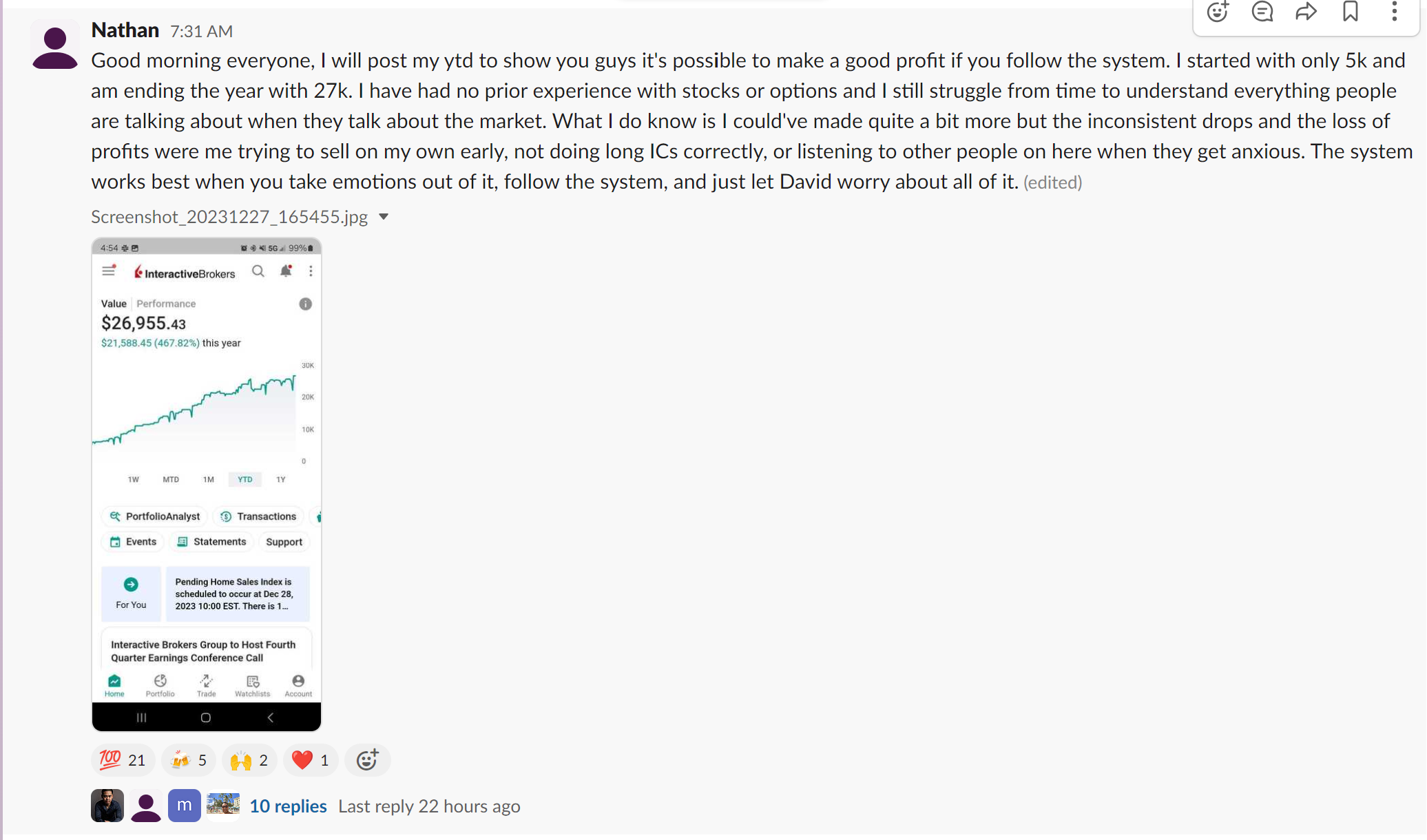
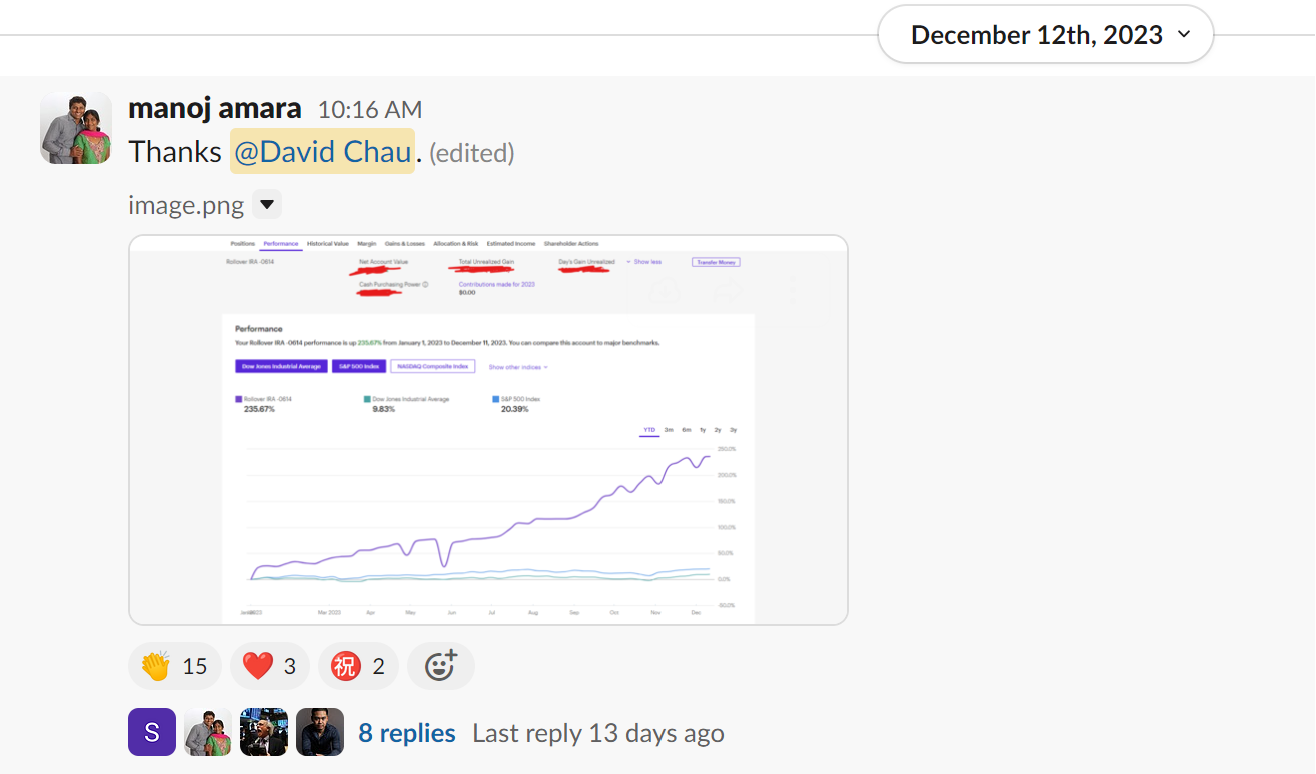
In the complex realm of options trading, Vertical Spreads are a popular and versatile strategy to help traders manage risks while still providing ample profit opportunities. At InsideOptions, we simplify trading for both experienced and novice traders alike by providing the knowledge, resources, and support needed to effectively comprehend, apply, and manage Vertical Spread strategies. With a solid grasp of the various Vertical Spread strategies, options traders can refine their trading approach, optimize their risk-reward profile, and achieve consistent success in the market.
Vertical Spreads are constructed by buying and selling options of the same type (calls or puts) with the same expiration date but different strike prices. By combining different option contracts, traders can create a sophisticated strategy that enables them to benefit from a variety of market conditions, whether they are bullish, bearish, or neutral. Additionally, the use of Vertical Spreads can help control the downside risks of options trading, making them an essential part of any well-rounded trading plan.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the intricacies of Vertical Spreads in options trading, discussing different Vertical Spread strategies such as Bull Call Spreads, Bear Put Spreads, Bull Put Spreads, and Bear Call Spreads. Furthermore, we will delve into trade setups, entry and exit criteria, and various techniques for managing Vertical Spread positions. With InsideOptions as your trusted partner, embrace the power of Vertical Spreads and unlock the doors to better risk management, enhanced decision-making, and consistent returns in options trading.
1. Market Orders: Fast and Straightforward Execution
Market orders are typically the simplest and most straightforward option order type in the trader’s arsenal:
– Characteristics: A market order is an instruction to buy or sell an options contract immediately at the best available market price. It prioritizes execution speed over price control, ensuring that a trade is filled promptly.
– Advantages: Market orders offer simplicity, speed, and a high likelihood of execution, making them suitable for fast-moving markets or situations where immediate execution is a priority.
– Disadvantages: Due to the lack of price control, market orders can potentially lead to suboptimal entry and exit prices, especially in volatile or illiquid markets, where price slippage is a concern.
2. Limit Orders: Targeting Specific Prices with Precision
Limit orders provide a higher level of price control by setting specific target entry and exit prices:
– Characteristics: A limit order is an instruction to buy or sell an options contract only at a specified price or better. This order type prioritizes price control over execution speed, ensuring that trades are executed at a specific price target or better.
– Advantages: Limit orders offer greater price control and enable traders to enter and exit positions at their desired price levels, potentially improving trade profitability.
– Disadvantages: With price targets in place, limit orders carry the risk of not being executed if the specified price is not reached, which may cause traders to miss potential opportunities.
3. Stop Orders: Mitigating Losses and Protecting Profits
Stop orders are crucial risk management tools designed to limit losses and lock in profits:
– Characteristics: A stop order activates a market order to buy or sell an options contract when the market price reaches a specified level. Stop orders can be used to minimize losses (stop loss orders) or protect profits (trailing stop orders).
– Advantages: Stop orders provide an automated mechanism for risk management, allowing traders to predefine exit points for loss minimization and profit maximization.
– Disadvantages: Stop orders are subject to price slippage, potentially leading to worse-than-expected exit prices, especially in fast-moving or volatile markets.
4. Conditional Orders: Advanced Execution Strategies for Sophisticated Traders
Conditional orders enable the execution of complex, multi-variable strategies tailored for experienced traders:
– Characteristics: Conditional orders, also known as contingent orders or multiple criteria orders, only activate when specific market conditions or price levels are met. These orders may combine several criteria such as time, price, and options Greek metrics to refine execution strategies.
– Advantages: Conditional orders offer flexibility and precision in execution, enabling traders to adapt to various market scenarios and construct sophisticated trading strategies.
– Disadvantages: Due to their complexity, conditional orders may be challenging to set up or modify, and can be subject to incomplete or unexpected execution if market conditions do not unfold as anticipated.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing various option order types is vital for traders seeking to excel in the competitive options market. By mastering market, limit, stop, and conditional orders, traders can optimize their execution strategies, manage risk effectively, and take advantage of opportunities for potential profit.
Leverage the insights and expertise provided by InsideOptions to enhance your options trading performance by employing different order types tailored to your unique trading needs. Through active learning and continuous improvement, traders can unlock their full potential in the dynamic world of options trading, reaching new heights of success and consistent profitability. Learn successful trading strategies here!